Massive Data Breach: Hacker Offers Access to 400+ Companies with Combined Revenue Over $1 Trillion
400+ companies affected by a breach, with access to critical tools up for sale. Is your company at risk? #DataSecurity #CyberAttack
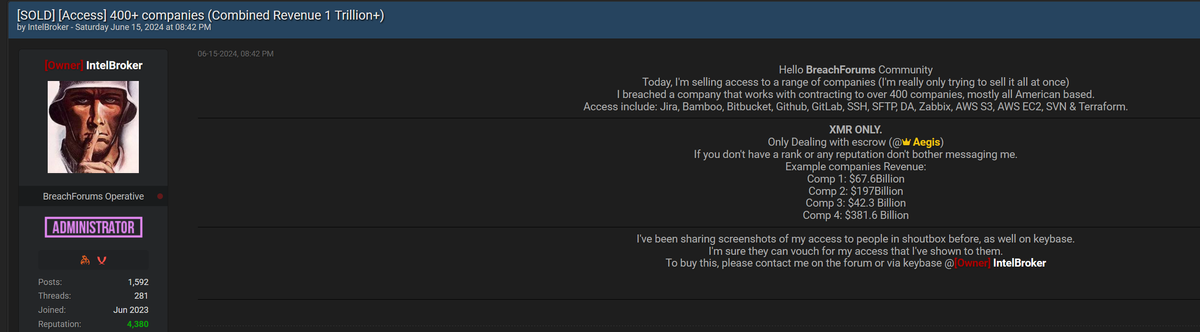
A significant data breach has surfaced on the dark web, with the notorious hacker IntelBroker at its center. On June 15, 2024, IntelBroker posted a chilling message on BreachForums, offering access to over 400 companies with a combined revenue exceeding $1 trillion. The hacker claims to have breached a company that contracts with these businesses, primarily American-based, and is now selling access to their internal systems.
The Breach: What Happened?
This breach involves unauthorized access to a company that manages contracts for hundreds of other enterprises. According to IntelBroker, the breach has provided them with deep access to a wide array of critical tools and services, including:
- Jira and Bamboo: Tools commonly used for project management and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
- Bitbucket and GitHub: Popular platforms for hosting and managing code repositories.
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): The leading cloud services platform, including S3 (Simple Storage Service) and EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud).
- Additional Tools: Including SSH, SFTP, Zabbix (for monitoring), SVN (Apache Subversion for version control), and Terraform (used for infrastructure as code).
The hacker has emphasized that this access is for sale, exclusively through Monero (XMR), a cryptocurrency known for its anonymity. Transactions will be conducted via an escrow service, ensuring security for both the buyer and the seller. IntelBroker has cited several examples of the companies impacted, with individual revenues ranging from $42.3 billion to $381.6 billion.
Who is IntelBroker?
IntelBroker is a well-known figure within the cybercrime community, particularly active on BreachForums. As an Administrator of the forum, IntelBroker has built a reputation for being a reliable source of high-value illicit data. With over 1,500 posts and a reputation score of 4,380, they have a history of involvement in significant data breaches, selling everything from personal information to corporate secrets and unauthorized access to critical systems.
Their methods typically involve exploiting vulnerabilities in enterprise software and cloud services, often targeting large companies with substantial digital footprints. This latest breach is consistent with their previous activities, showcasing their ability to infiltrate and monetize access to major corporations.
Potential Impact of the Breach
The scale of this breach is massive, with the potential to affect hundreds of companies, many of which are large enterprises with significant revenues. The sale of access to these companies' internal systems could lead to:
- Theft of Intellectual Property: With access to code repositories like GitHub and Bitbucket, attackers could steal proprietary code or other valuable intellectual property.
- Business Disruption: Project management tools like Jira could be manipulated to disrupt ongoing projects, leading to delays and financial losses.
- Further Security Breaches: Access to AWS environments could be used to launch additional attacks or deploy malicious software across the company's cloud infrastructure.
- Reputational Harm: Public disclosure of this breach could severely damage the reputations of the affected companies, especially if customer data is compromised.
Given the combined revenue of over $1 trillion, the economic impact of this breach could be profound, potentially affecting industries on a global scale.
How Companies Can Protect Themselves
In light of this breach, companies should consider taking several proactive measures to protect themselves:
- Enhanced Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of all critical systems is essential, particularly those related to software development and cloud services.
- Stringent Access Controls: Implementing strict access controls, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enforcing the principle of least privilege, can help reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits of all systems, particularly those managed by third-party contractors, can help identify and fix vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Planning: Having a robust incident response plan in place is crucial for quickly responding to and mitigating the effects of a breach.




